Why You Should File a Tax Extension
- March 11, 2024
- Posted by: CKH Group
- Category: Tax tips

Why You Should Consider Filing a Tax Extension
Filing a tax extension is a strategic move that provides numerous advantages, contrary to some common misconceptions. With tax deadlines getting closer, we’ve compiled a guide for you as to what tax extensions are, the list of benefits for filing a tax extension, and how to file an extension, should you choose to.
What is a tax extension?
A tax extension is an option selected by taxpayers or tax preparers that grants the taxpayer six more months to file their return (but you must still pay your taxes on time). For example, an individual tax filer will then have until October 15 to file a return, and S-corporations will have until September 15 to file a return (Dates may vary due to falling on the weekend or public holidays). Having this extension offers valuable opportunities and safeguards for taxpayers.
Is filing a tax extension bad?
 We are often asked if filing an extension will somehow draw additional scrutiny to a tax return or diminish the taxpayer’s standing in the eyes of the IRS. The answer is an emphatic “no!” This is a common misconception. In reality, filing an extension is a common practice employed by individuals and businesses alike to ensure compliance with tax laws while allowing for adequate time to gather necessary documentation and information. By extending the filing deadline, taxpayers can alleviate the pressure associated with rushing through the tax preparation process, thereby reducing the likelihood of errors or oversights.
We are often asked if filing an extension will somehow draw additional scrutiny to a tax return or diminish the taxpayer’s standing in the eyes of the IRS. The answer is an emphatic “no!” This is a common misconception. In reality, filing an extension is a common practice employed by individuals and businesses alike to ensure compliance with tax laws while allowing for adequate time to gather necessary documentation and information. By extending the filing deadline, taxpayers can alleviate the pressure associated with rushing through the tax preparation process, thereby reducing the likelihood of errors or oversights.
Moreover, filing a tax extension does not impact an individual’s or business’s standing with the IRS. The extension merely extends the deadline for filing the tax return, providing additional time to file (but not additional time to pay). In fact, the IRS encourages taxpayers to file for an extension if they need more time to complete their returns, emphasizing the importance of accuracy and thoroughness in tax reporting.
You will only experience these negative impacts if you do not pay on time or the full amount. Always remember that an extension is only an extension to file and not an extension to pay.
5 Benefits to Filing an Extension
There are many benefits to filing an extension, most notably that it will help you avoid penalties, reduce the likelihood of costly errors, provide more streamlined tax filing, address unforeseen changes, and give the opportunity to leverage tax credits and deductions to their maximum potential.
1. Protection Against Late Filing Penalties
One of the primary benefits of filing a tax extension is the protection it provides against late filing penalties. By extending the filing deadline, taxpayers can avoid hefty financial penalties that may accrue for failing to submit their tax returns on time. Again, it’s extremely important to recognize that an extension grants additional time for filing, not for payment, meaning any tax liability is still due by the original deadline, or the tax payer will incur penalties.
What are the late filing penalties?
Typically, the late filing penalty is a percentage of how much you owe and with consideration to how much was submitted already.
- Failure to settle the entirety of your owed sum will result in the IRS applying interest on the outstanding balance until it is settled completely.
- Additionally, if you fail to pay at least 90% of the total owed amount, you may also face a late payment penalty. This penalty typically equates to half of 1% of the amount owed per month, capped at 25%.
- Furthermore, neglecting to submit either your tax return or Form 4868 by the designated tax filing deadline for the applicable tax year will incur a late filing penalty. This penalty usually amounts to 5% of the owed sum for each month, with a maximum penalty of 25%.
2. Leveraging Superseding Returns for Flexibility
A benefit some might not be aware of is that filing an extension opens the door to superseding returns, offering taxpayers enhanced flexibility and simplicity in the filing process, should you need to make changes to a return.
Superseding Vs Amended Returns
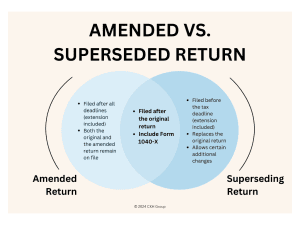
Usually, once you file a tax return, any change or omission must be reported on an amended return. However, if you’ve filed an extension, you would instead file a superseding return that replaces the original.
The difference is that with an amended return both the original and the amended return are on record, but with a superseded return you are replacing the original return, and only it return remains on record. This is why your tax preparer might suggest filing an extension, even if they are confident your return will be prepared by the original deadline.
This streamlined approach ensures that only the most recent filing remains on record, reducing confusion and administrative burden for both you and your tax preparer in future. Keep in mind, the easier your tax filing is, the more likely it is (but not guaranteed) that you will save time or money on tax preparation services.
3. Addressing Unforeseen Tax Obligations
Additionally, filing a tax extension offers the flexibility to address unforeseen circumstances or changes in financial circumstances. Whether dealing with unexpected life events, changes in employment status, or complex financial transactions, an extension provides the time needed to assess the impact on tax liability and make informed decisions. In many cases, taxpayers may become aware of additional income or financial activities later in the year, requiring the submission of supplemental documentation. Filing an extension allows for thorough review and compliance with all necessary reporting requirements, minimizing the risk of penalties or audits.
In fact, if your tax preparer is made aware of these major tax changes too close to the deadline, they will most likely need to file an extension regardless in to correctly and accurately file your return.
4. Correcting Errors and Adjustments
One of the key benefits to extending the filing deadline is that it offers taxpayers and their tax preparers the opportunity to review returns thoroughly and correct any errors or adjustments. This additional time provides more confidence that tax returns are accurate and complete, reducing the likelihood of errors or discrepancies that could trigger IRS inquiries or audits. Moreover, taxpayers may discover new tax-saving opportunities or deductions during the review process, enabling them to make informed decisions and optimize their tax outcomes.
5. Optimize Tax Planning with Extended Time
By filing a tax extension, taxpayers gain valuable time to explore tax-saving strategies and maximize deductions and credits. With the extended deadline, individuals and businesses can engage in comprehensive tax planning, identifying opportunities to minimize tax liabilities and maximize refunds. There are dozens of credits or deductions you may apply for, and this extended time gives you are your tax preparer the opportunity to leverage them. View our articles to read more about refundable and nonrefundable tax credits. This proactive approach allows taxpayers to leverage available tax incentives, implement strategic financial decisions, and achieve optimal outcomes in their tax filings.
How to File a Tax Extension
To ensure you have filed your tax extension, you must complete Form 4868, either electronically or via mail, and submit it to the IRS by the original tax filing deadline (April 15 for individuals). If you estimate your taxes owed and make a payment online by tax day, specifying that it’s for an extension, and you can bypass the paperwork entirely.
Otherwise, here are the most common methods for filing a tax extension:
- Tax preparer: Arguably the easiest way to file a tax extension is by inquiring with your tax preparer that they file it on your behalf. Just make sure that if they require any additional information from you that you respond on time before the deadline. CKH Group can handle this step for you, so you don’t need to worry about filing an extension before the deadline.
- IRS Free File: Utilize the IRS’s partnership with the Free File Alliance, offering free tax-prep software for individuals with an adjusted gross income of $79,000 or less. Even those exceeding the income threshold can access free extension filing online via the IRS website.
- Tax software: Many tax software platforms support Form 4868 for tax extensions. Simply follow the software’s prompts to file electronically, and upon submission, the IRS will send an electronic acknowledgment.
- Mail submission: For a paper filing, complete Form 4868 and mail it to the IRS. Ensure it’s postmarked by the original tax deadline (April 15 for individuals) and retain proof of mailing for your records.
If you have any questions or concerns about filing a tax extension, CKH Group is here to help you! You can reach out here to book a free consultation or you can call us at 1-770-495-9077 or email us at [email protected]
The above article only intends to provide general financial information and is based on open-source facts, it is not designed to provide specific advice or recommendations for any individual. It does not give personalized tax, financial, or other business and professional advice. Before taking any form of action, you should consult a financial professional who understands your particular situation. CKH Group will not be held liable for any harm/errors/claims arising from the articles. Whilst every effort has been taken to ensure the accuracy of the contents we will not be held accountable for any changes that are beyond our control.
